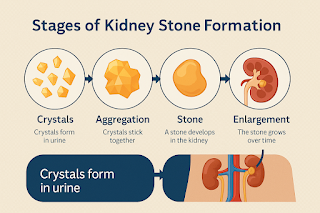
Introduction
Imagine waking up to a sharp, stabbing pain in your lower back. You rush to the bathroom, only to find blood in your urine. The agony is unbearable. You're not alone. Approximately 1 in 10 Americans will experience a kidney stone in their lifetime .
What Are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form inside your kidneys. They can affect any part of your urinary tract and often cause severe pain when passing through.(self.com)
Prevalence in the U.S.
-
Overall prevalence: 8.8% (journals.lww.com)
-
Men: 10.6%; Women: 7.1% (pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
-
Higher prevalence among obese individuals (pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
Symptoms
Common signs include:(pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
-
Severe, sharp pain in the side and back, below the ribs(mayoclinichealthsystem.org)
-
Pain that radiates to the lower abdomen and groin(mayoclinichealthsystem.org)
-
Pain that comes in waves and fluctuates in intensity(mayoclinichealthsystem.org)
-
Pain or burning sensation while urinating(mayoclinichealthsystem.org)
-
Pink, red, or brown urine
-
Cloudy or foul-smelling urine(mayoclinic.org)
-
Persistent need to urinate, urinating more often than usual, or urinating in small amounts(mayoclinichealthsystem.org)
-
Nausea and vomiting(mayoclinichealthsystem.org)
-
Fever and chills if an infection is present
Causes
Kidney stones form when your urine contains more crystal-forming substances than the fluid can dilute. Factors include:(verywellhealth.com)
-
High levels of calcium, oxalate, and uric acid
-
Low urine volume due to dehydration
-
Diet high in protein, sodium, or sugar
-
Obesity and certain medical conditions
Types of Kidney Stones
-
Calcium Stones: Most common, often in the form of calcium oxalate.
-
Uric Acid Stones: Form in people who lose too much fluid or eat a high-protein diet.
-
Struvite Stones: Can form after a urinary tract infection.
-
Cystine Stones: Form in people with a hereditary disorder that causes the kidneys to excrete too much of certain amino acids .(eatingwell.com)
Treatment Options
-
Hydration: Drinking water helps flush out the urinary system.
-
Medications: Pain relievers and medications to help pass stones.
-
Medical Procedures
: Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), ureteroscopy, or percutaneous nephrolithotomy for larger stones .
Prevention Tips
-
Stay Hydrated: Aim for at least 2–3 liters of water daily.
-
Dietary Changes: Reduce sodium, limit animal protein, and avoid high-oxalate foods.
-
Calcium Intake: Consume adequate calcium through diet to bind oxalate.
-
Limit Sugar and Soda: Excessive sugar and soda intake can increase risk .
Reliable Sources for Further Information
Understanding kidney stones, their causes, and prevention strategies can help reduce the risk and manage symptoms effectively.